Description
Quantum Cascade Lasers (QCL) are designed for the MIR spectral range from 4µm to 12µm. QCLs enable access to wavelengths which are important for molecule spectroscopy.
Technical Details
Description:
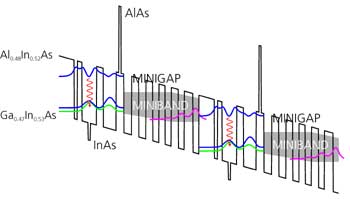
Quantum Cascade Lasers (QCL) are designed for spectroscopy in the MIR spectral range. A schematic description of the gain mechanism is given in the drawing. Opposite to conventional diode lasers, the optical gain is generated via an interband transition of the conduction band. With this band gap design, wavelengths in the MIR spectral region are accessible for spectroscopy applications.
Available Wavelength:
Room temperature CW operational Quantum Cascade Laser are available from from 4.4µm up to 9.5µm. Further wavelength may be available upon request.
Wavelength Section Types:
Quantum Cascade Lasers are available as longitudinally single-mode as well as longitudinally multi-mode devices:
- Fabry Perot Quantum Cascade Lasers (FP QCLs) operate logitudinally multi-mode and offer high output power.
- Distributed Feedback Quantum Cascade Lasers (DFB QCLs) operate longitudinally single-mode with sightly reduced output power in comparison to the FP models.
Types of Quantum Cascade Lasers:
There are currently several different types of Quantum Cascade Lasers available on the market:
- Pulsed Quantum Cascade Lasers, which will be operated in a short pulse mode with a typical pulse duration of 150ns.
- CW Quantum Cascade Lasers, which will be operated in a continuous emission mode.
Pulsed Quantum Cascade Lasers enable a fast wavelength tuning (c/f our publications) whereas CW Quantum Cascade Laser enable a higher wavelength precision.
Measurements with Pulsed Quantum Cascade Lasers:
Pulsed operated Distributed Feedback Quantum Cascade Lasers (DFB QCLs) show a temperature tuning during the pulse duration. This effect is caused by a change of the temperature within the active area due to the injected current. The benefit of this effect for technical applications is an automatic wavelength tuning. The above figue shows the behavior of a pulsed DFB QCL. The lower trace is a reference curve which shows the transmission ripple of an etalon. The upper traces show the intensity behavior of the DFB QCL. The dip within the broken lines of the upper trace is caused by the absoption of NO. In summary, a pulsed Distributed Feedback Quantum Cascade Laser System is a ready to use spectroscopic instrument.

Typical applications for this type of Quantum Cascade Lasers are:
- Single Species Detection
- Concentration Measurements of Single Species
- Production Supervision and Quality Control in Chemical Production Plants
Measurements with CW DFB Quantum Cascade Lasers:
CW operated Distristributed Feedback Quantum Cascade Lasers (DFB QCLs) show a significantly lower linewidth than pulsed DFB QCLs. The principles of measurement as equivalent to the principles of measurement of conventional diode lasers. Typically the case temperature of the DFB QC Laser is preset to the required wavelength. The fine tuning is performed via a laser current modulation. This type of measurement enables higher precision measurements than the pulsed measurement scheme. Typical applications are:
- Single Species Detection
- High Precision Concentration Measurements of Single Species
- Production Supervision and Quality Control in Chemical and Pharmacutical Production Plants
Measurement with External Cavity Quantum Cascade Lasers:
External Cavity Tunable Quantum Cascade Lasers show a significantly higher spectral tuning range than DFB Quantum Cascade Lasers. Typically, a Littrow or a Littman/Metcalf Cavity is choosen as cavity design. The external cavity enables a tuning range of greater than 100 wavenumbers. Typical applications include:
- Multi Species Detection
- High Precision Concentration Measurements of Single or Multiple Species within a Multi Species Enviroment
- Production Supervision and Quality Control in Chemical Production Plants
- Production Supervision and Quality Control in Pharmacutical Production Plants
- Trace Gas Detection
- Bio-medical Analysis
- Patient Supervision
Application Notes
Sacher Lasertechnik offers a large collection of application notes on external cavity diode lasers as Absorption Spectroscopy, Raman Spectroscopy, Metrology and Fluorescence Spectroscopy.
Technical Notes
Sacher Lasertechnik offers a large collection of technical notes which are downloadable as PDF Files.
Publications
Sacher Lasertechnik offers a large collection of Sacher publications or publications where Sacher equipment has been used. All documents are downloadable.
Acknowledgement:
We gratefully acknowledge financial support by the BMBF with contract FK13N8020 and the technical support of the project partners Fraunhofer IAF and Fraunhofer IPM.
Support & Download
Publications
- Quantum cascade external cavity and DFB laser systems in the mid-infrared spectral range: Devices and applications (LACEA 2004)L. Hildebrandt, S. Stry, R. Knispel, J. R. Sacher, T. Beyer, M. Braun, A. Lambrecht, T. Gensty, W. Elsäßer, Ch. Mann, F. Fuchs, LACEA Conference, Anapolis, MD 2004
- Quantum cascade external cavity laser systems in the mid-infrared spectral rangeL. Hildebrandt, S. Stry, R. Knispel, J. R. Sacher, Ch. Mann, F. Fuchs, CLEO Conference, San Francisco, CA 2004

 Laser Diode and DPSS Laser system
Laser Diode and DPSS Laser system High Power Tunable External Cavity Diode Lasers
High Power Tunable External Cavity Diode Lasers Nd:YAG Laser Systems
Nd:YAG Laser Systems Spectral Products & CVI Laser
Spectral Products & CVI Laser Excimer Lasers
Excimer Lasers Synrad Lasers
Synrad Lasers  Gauge Calibration Instruments
Gauge Calibration Instruments Corning Tropel Interferometer system
Corning Tropel Interferometer system Mask Aligner & Spin Coater equipment
Mask Aligner & Spin Coater equipment PCO Imaging High Performance Camera system
PCO Imaging High Performance Camera system Customer Laser Spectroscopy and High Resolution Imaging System
Customer Laser Spectroscopy and High Resolution Imaging System Cryogenic
Cryogenic


